Research: Evading Portspoof Solution
Introduction
One of the opensource solutions caught my eyes before and it was preventing and making port scanning hard to be done against the target that running it. Now, we will discuss how to evade it.
What is portspoof ?
Portspoof is meant to be a lightweight, fast, portable and secure addition to the any firewall system or security system. The general goal of the program is to make the reconnaissance phase slow and bothersome for your attackers as much it is only possible. This is quite a change to the standard 5s Nmap scan, that will give a full view of your systems running services. (Read More)
Testing Lab
I used Ubuntu Server as a victim & kali linux machine as attacker. If you faced any problems with installing Portspoof. You may install the needed packages/libraries:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install gcc g++ make libc6-dev libc6-dev-i386
Installation
-
Note:
Don't forget to run all commands as sudo in new versions of linux. So, you avoid problems You can install portspoof from the following blog.Click Here. or From the following commands: -
Download Portspoof:
git clone https://github.com/drk1wi/portspoof.git
- Compile Portspoof:
sudo ./configure && make && sudo make install
-
Now, the following commands are used in specific situations.
-
The first one is to redirect all connections to portspoof
sudo iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -i eth0 -p tcp -mtcp --dport 1:65535 -j REDIRECT --to-ports 4444 -
The second one is to redirect some range of ports and exclude the real running services ports, For example, the following command not including port
22and80
sudo iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -i eth0 -p tcp -m tcp -m multiport --dports 1:21,23:79,81:65535 -j REDIRECT --to-ports 4444
-
Here is a bash script that you can use to configure and automate this process and don’t forget to exclude the real running services ports:
#!/bin/bash
spoofPorts="1:19 23:24 26:52 54:79 81:109 112:122 124:442 444:464 466:586 588:891 893:2048 2050:8079 8081:32800 32801:65535"
for prange in ${spoofPorts}; do
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -i eth0 -p tcp -m tcp --dport ${prange} -j REDIRECT --to-ports 4444
done
This bash script sets up iptables rules to redirect incoming traffic on certain ports to port 4444 (Which is port spoof listening port). The variable “spoofPorts” contains a list of port ranges separated by spaces, in the format “startPort:endPort”. Then uses a for loop to iterate through each port range in the spoofPorts variable. For each iteration, the script runs the iptables command, which creates a new rule in the NAT table’s PREROUTING chain. The rule specifies that incoming traffic on interface eth0, using the TCP protocol, and destined for one of the ports in the current range, should be redirected to port 4444.
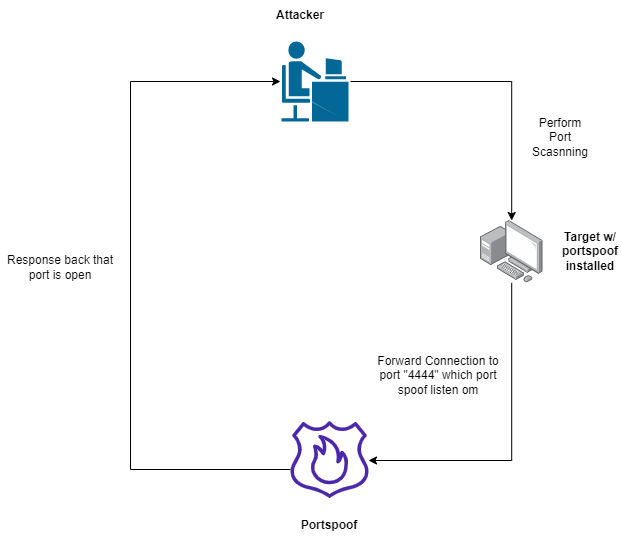
How Portspoof works ?
Portspoof got a huge number of signatures when you connect to any port as we configured before in iptables it will forward all connections to portspoof services and will response with [syn-ack] that the ports are open. Then we won’t be able to identify the real services. Also, portspoof is responsing with banners etc. So, its hard to identify the actual running real services. But, portspoof is not affecting the actual real running services ( as we configured in the bash script ).
Portspoof working steps:
1- Attacker perform port scanning using nmap
2- The victim machine look at the iptables rules and forward the connection to portspoof services
3- portspoof response with [syn-ack]
4- Nmap identify ports as open and running
5- attacker try to enumerate version of protocols & banners
6- portspoof response based on the config & signatures (which is fake)
7- Nmap output based on the portspoof response
Traffic Analysis
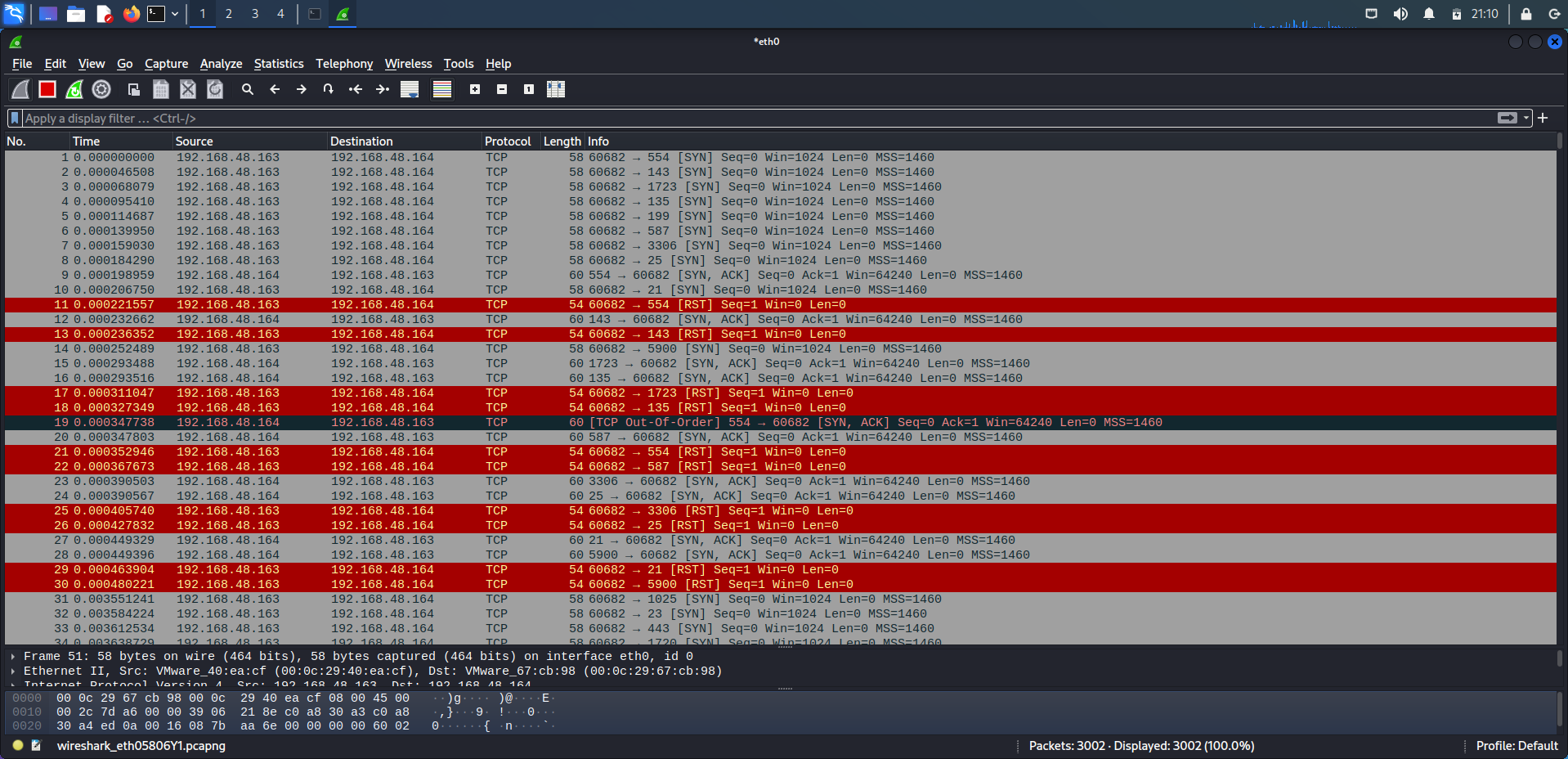
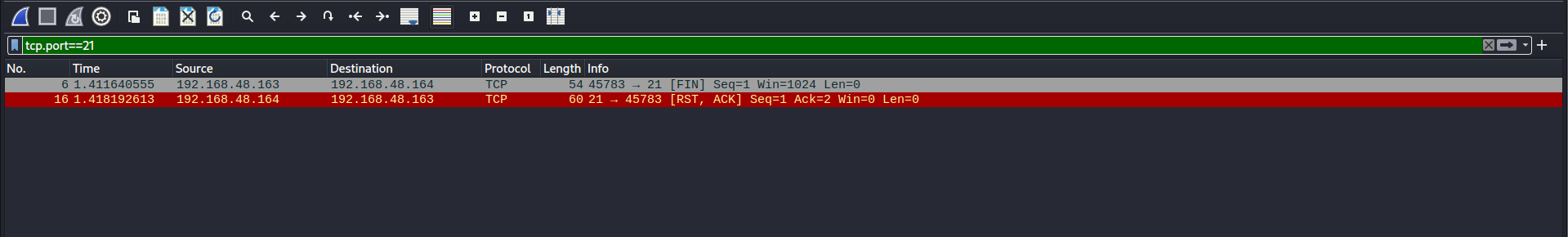
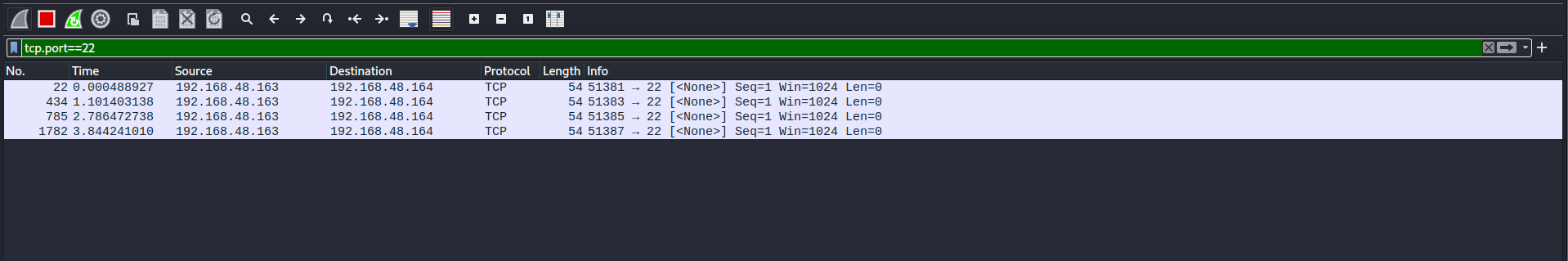
The following pictrue shows the normal nmap scan. Now, on this target at te moment ssh services are running on port 22.
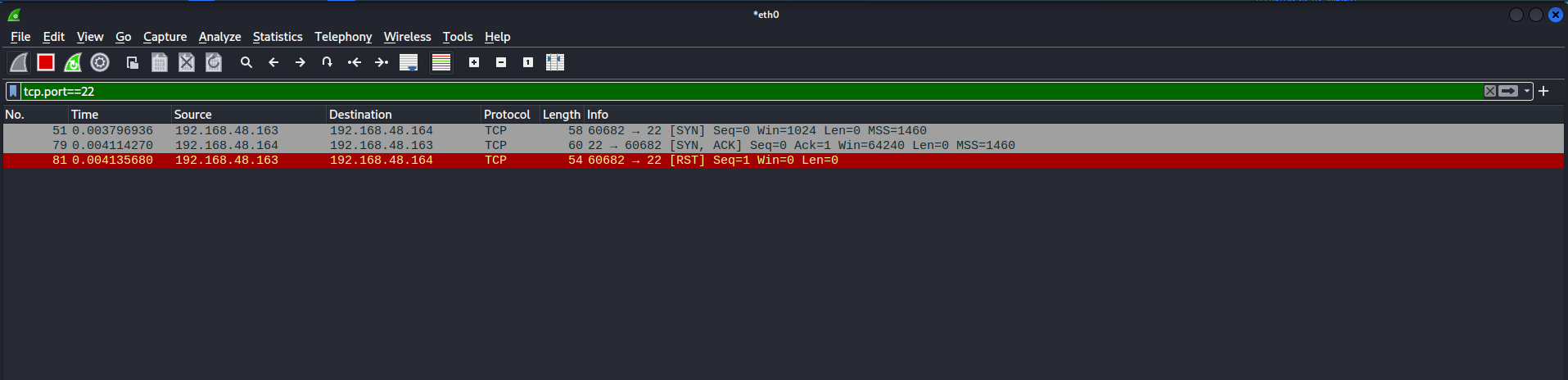
So, if we used the tcp.port==22 filter in wireshark to take a look on how nmap identified the ssh as it’s running and it’s a real services.
We can see clearly that the normal scan of nmap, Just looking for any response from the target and then identify it as running/open.
But, if we tried other types scannings it will work (Not all types). For example Fin Scan, Null Scan.
-
Fin Scan:
-
Open Port
-
Closed Port
-
-
Null Scan:
-
Open Port
-
Closed Port
-
But, nmap and related scans are known and can be caught by any measure of defense like IDS/IPS. So, Let’s complete by doing it manually.
Evading Portspoof
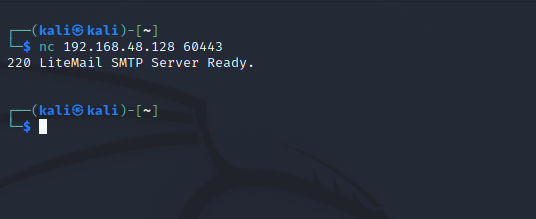
We need to know how portspoof is dealing with our connections. So, we will be able to generate a bypass scenario. Lets try to connect manaual using netcat or telnet. I have used netcat but the connection were closed by the host without waiting any input from me for a reason.
netcat:
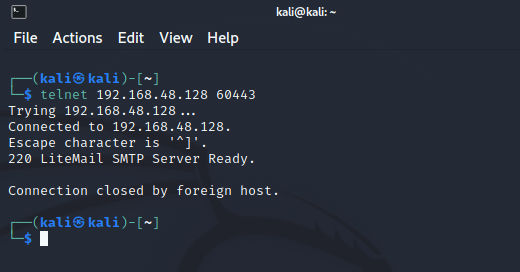
I tried telnet after that and the connection is closed by the host (victim):
As we can guess from this that portspoof just creating the banners and response and close the connection.
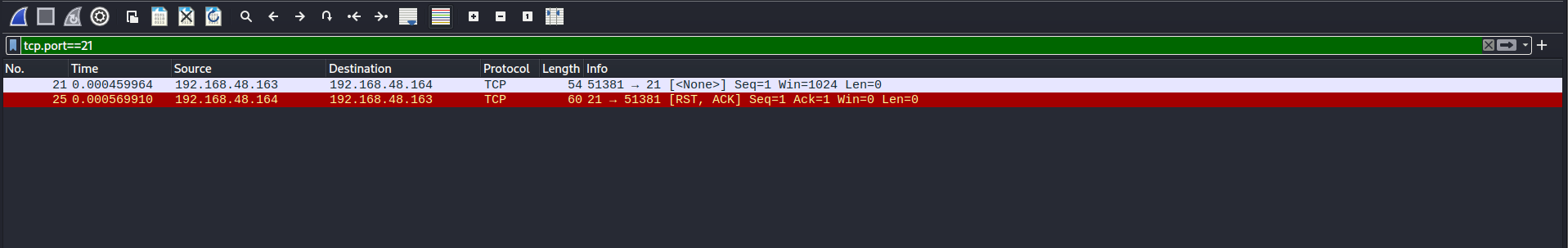
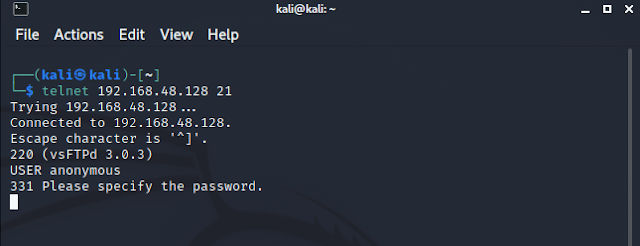
The victim got port 21 (ftp) open by default so lets try to connect it.
As you can see the real services didn’t close the connection. Then for sure the fake one close the connection. Steps to identify the real running services:
1- Connect to the service
2- if we receive data and services closed connection then its fake
3- if we received data and send any command and received another data then its real service or the connection didn't closed then it's a real service
Automate the process
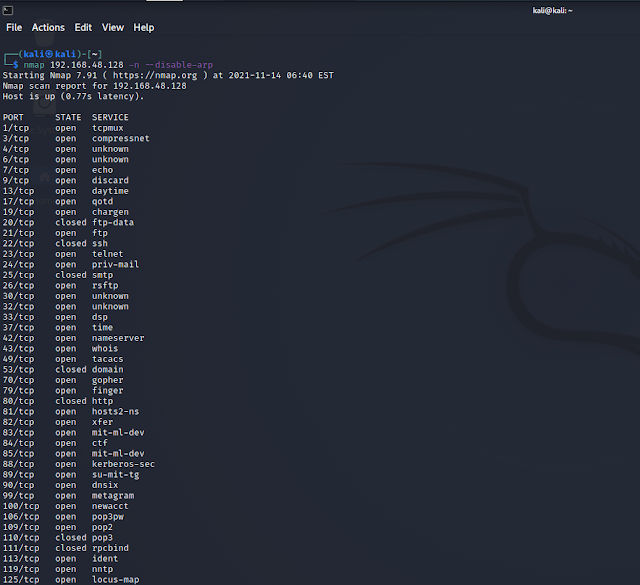
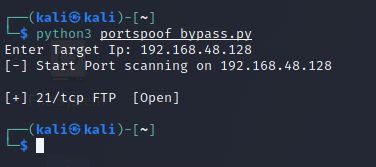
We gonna automate the process using python and we gonna try it on FTP services. But, First lets try to scan with nmap.
As you can see its a miss and most of the ports identified as open and few as closed. So, we gonna use the following script to test it.
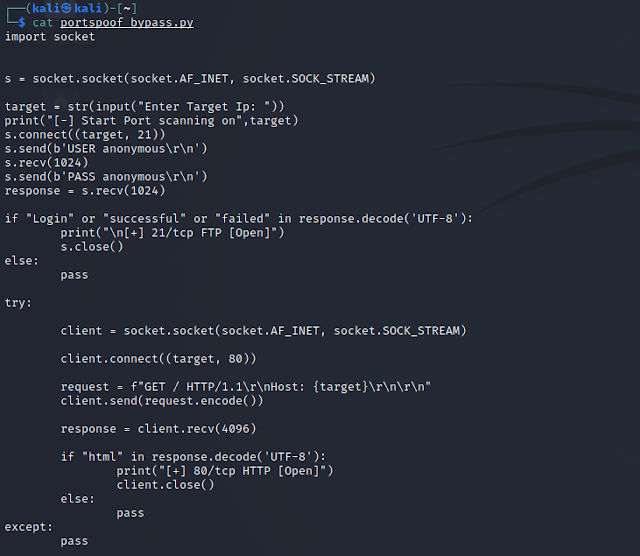
Script:
To avoid false positives we gonna use the commands of each protocol and we gonna try with ftp & http protocols. The script is creating a connection with ftp services first, receive response then try to login with anonymous and receive the second response and save it in response variable. After that is comparing if the response contains the Login word cause when we try to login in FTP is printing Login word in each fail and success try. If the Login is exist it will identify the services as open else is gonna just pass it. The same for the HTTP services but its checking if the html word is exist in the response. Now let’s run it:
We got the ftp port as opened. Now you know how to bypass it you can write your tool on your own way to identify the services that you want or to identify if the connection is alive or no.
Conclusion
As we were able to see it was simple way to bypass it using the workflow or the logic behind it. Therefor, we will be able to break it with no doubts and reach the real used ports on the system and start our next steps in our Pentesting project.