CVE-2021-42890: Hostime Remote Command Injection
Introduction
A vulnerability discovered in TOTOLINK EX1200T model known as CVE-2021-42889 which is a remote command injection through the HostTime parameter, As a results a malicious user can control the device and achieve remote command execution RCE. (Note:Everything you obtain here is for educational purposes, Don't use or abuse any bug against any target without permissions)
Obtaining the Firmware
Before we start we would need the firmware of the device, The
refore We can take a static look at the code and how it works to understand more. So, what we need is the vulnerable Firmware for the device which is V4.1.2cu.5215 and we have many ways to do it:
-
You can search for the firmware on the official website for the vendor.
-
Download it from any other source (after someone already dump it from the device and published it).
-
Dump the firmware through
UART, You could read a detailed blog from Here. -
Also, you could contact the support to provide you with the firmware.
-
Finally dumping the firmware using
CH341AMini programmer USB, You could read a detailed blog from Here.
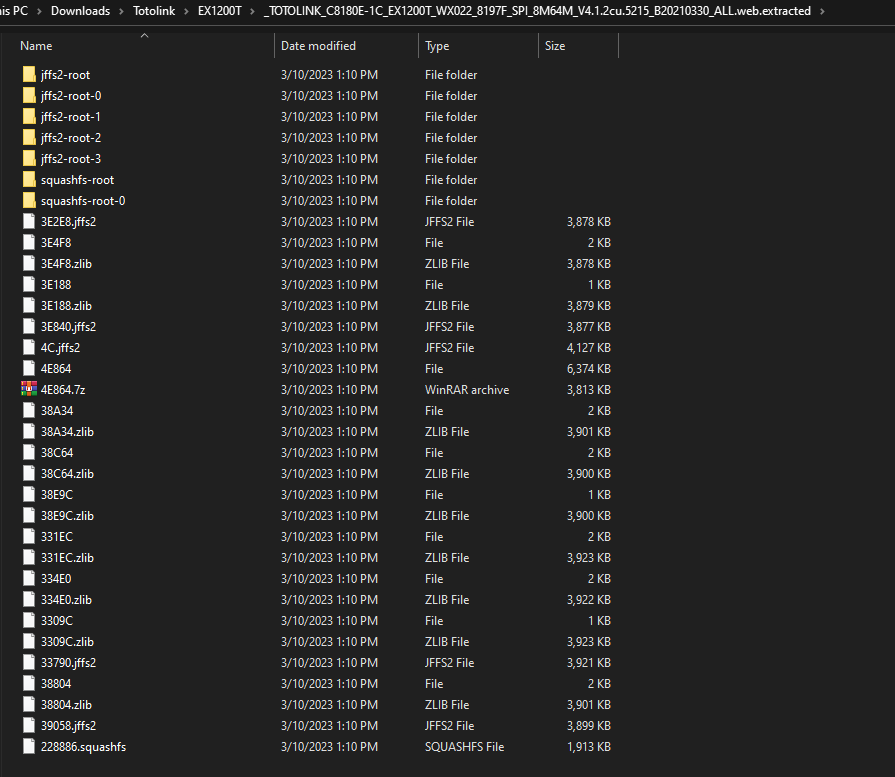
In my case, I found the firmware on the vendor website. Now, Let’s extract the firmware using binwalk tool as the following binwalk -e --run-as=root "TOTOLINK_C8180E-1C_EX1200T_WX022_8197F_SPI_8M64M_V4.1.2cu.5215_B20210330_ALL.web" and here is the output:
$ ls
TOTOLINK_C8180E-1C_EX1200T_WX022_8197F_SPI_8M64M_V4.1.2cu.5215_B20210330_ALL.web
$ sudo binwalk -e --run-as=root "TOTOLINK_C8180E-1C_EX1200T_WX022_8197F_SPI_8M64M_V4.1.2cu.5215_B20210330_ALL.web"
[sudo] password for azima:
DECIMAL HEXADECIMAL DESCRIPTION
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
76 0x4C JFFS2 filesystem, little endian
209052 0x3309C Zlib compressed data, compressed
209388 0x331EC Zlib compressed data, compressed
210144 0x334E0 Zlib compressed data, compressed
210832 0x33790 JFFS2 filesystem, little endian
231428 0x38804 Zlib compressed data, compressed
231988 0x38A34 Zlib compressed data, compressed
232548 0x38C64 Zlib compressed data, compressed
233116 0x38E9C Zlib compressed data, compressed
233560 0x39058 JFFS2 filesystem, little endian
254344 0x3E188 Zlib compressed data, compressed
254696 0x3E2E8 JFFS2 filesystem, little endian
255224 0x3E4F8 Zlib compressed data, compressed
256064 0x3E840 JFFS2 filesystem, little endian
321636 0x4E864 LZMA compressed data, properties: 0x5D, dictionary size: 8388608 bytes, uncompressed size: 6526520 bytes
And as i am using Windows Subsystem Linux (WSL), Here we can browser our firmware normally:
The Analysis
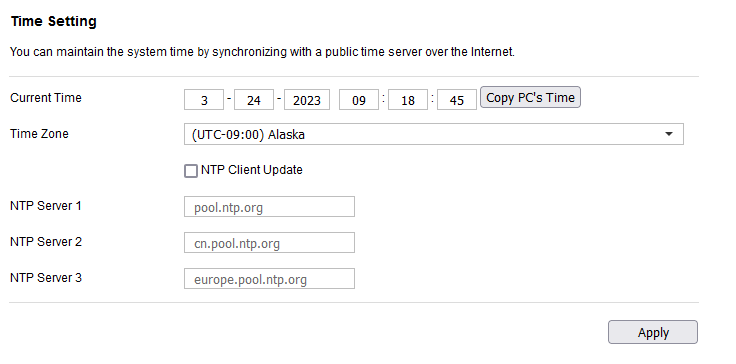
It’s the time for the analysis. We will need Burp Suite to see how is the request made that contains HostTime parameter where the command get injected. In the Time Setting Under Management tab, We can notice Copy PC's Time:
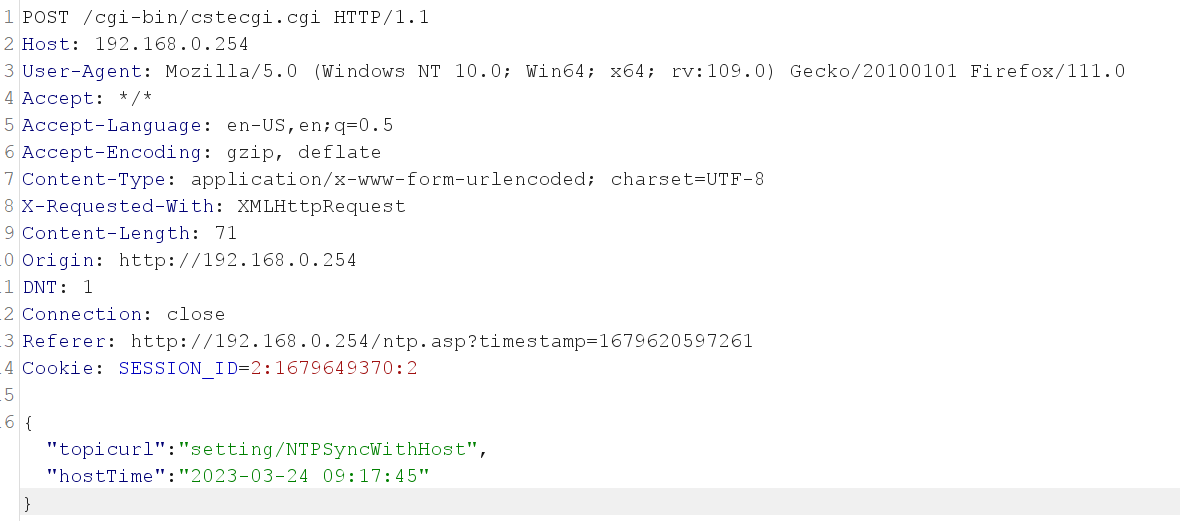
By clicking on it we can see the following request made to cstecgi.cgi:
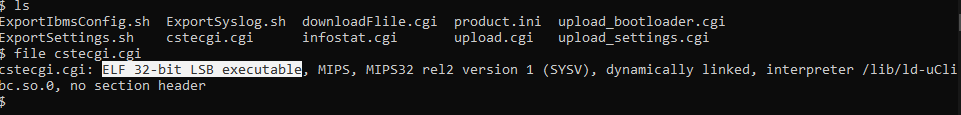
Let’s go with Ghidra and reverse the cstecgi.cgi file. Now, By going to the file and check it with the file command, We can see it’s an ELF 32bit MIPS file:
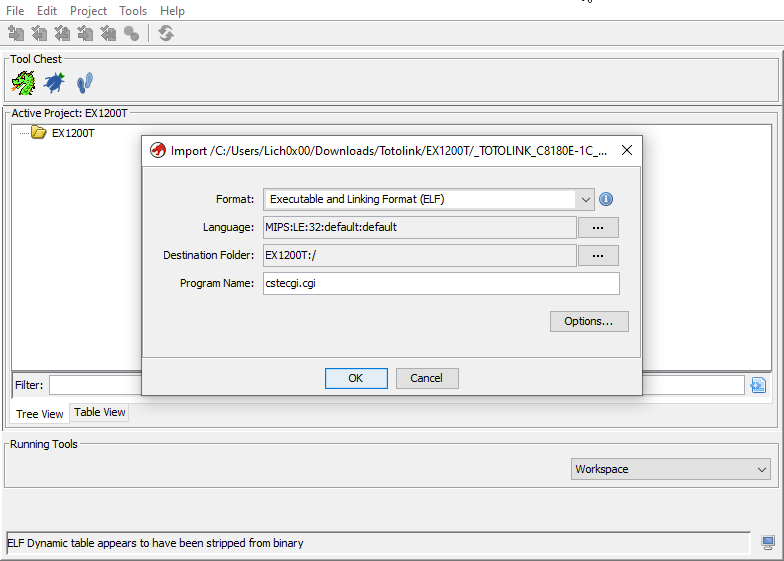
Open it and create a new project i named it EX1200T for the device name and drop the cstecgi.cgi file into the project:
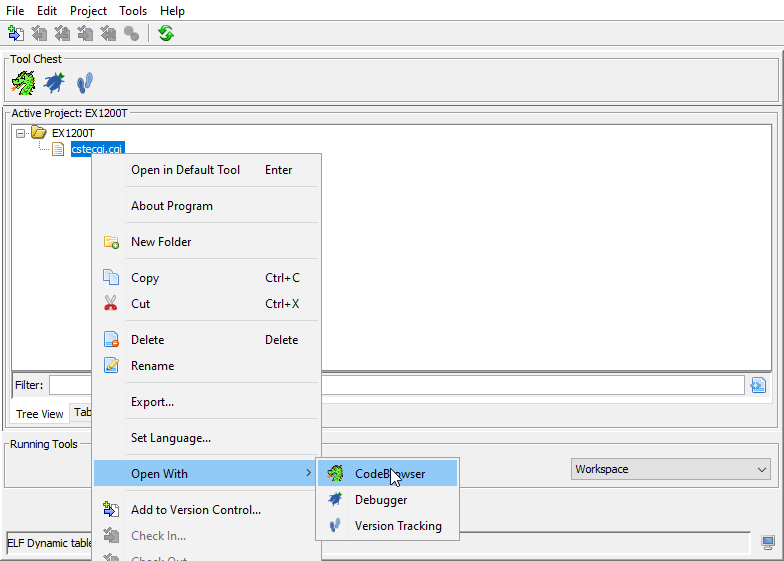
After that open the file using Code Browser within Ghidra:
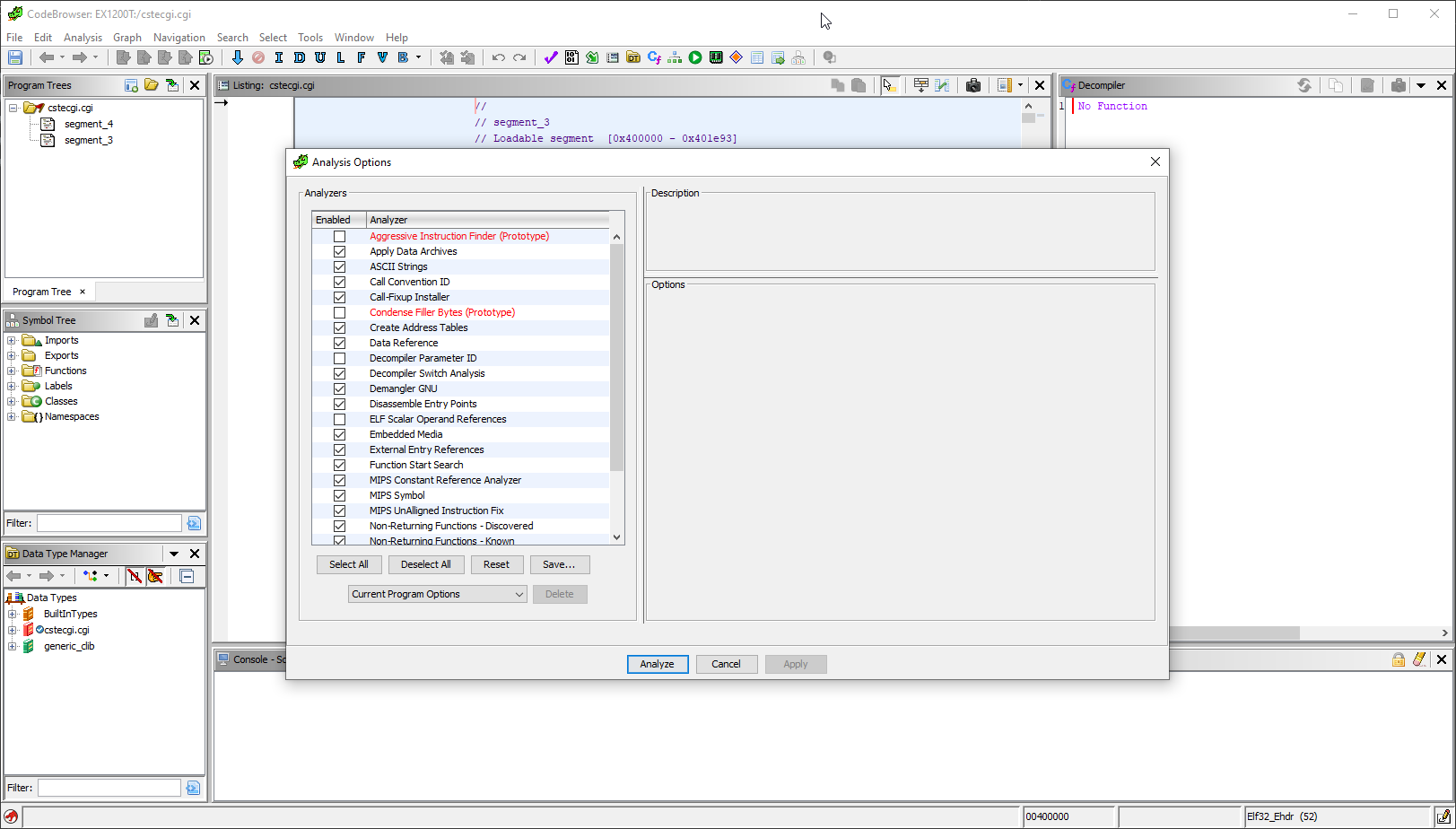
Then, analysis the file:
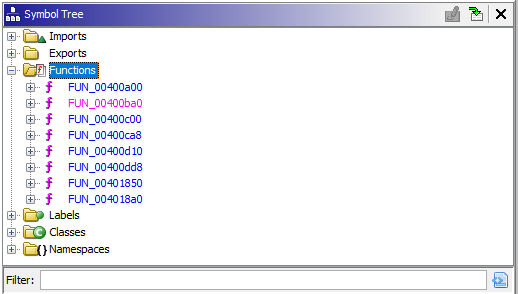
Navigating to Symbol Tree and let’s check out the functions:
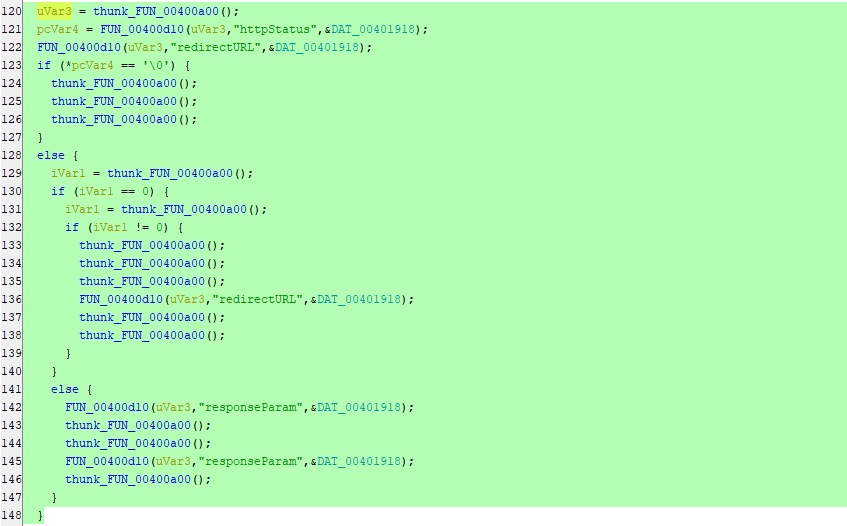
After going through the functions clearly inside FUN_00400dd8 function we can see the following lines of codes. But, there is no thing interesting and it’s all about functions calling other functions:
We just can see that httpStatus, redirectURL & responseParam being passed to some unclear functions. But, You can see under \squashfs-root\lib\cste_modules folder that there are libraries named as the following:
app.so
cloudupdate.so
global.so
lan.so
product.so
system.so
upgrade.so
wireless.so
wps.so
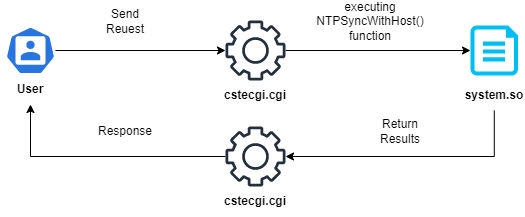
After reversing this libraries you will know that it’s clearly used by the cstecgi.cgi to perform different operations and changes through the device panel. Let’s identify which one contains the NTPSyncWithHost by searching through the following Bash one liner using strings command:
for i in $(ls -la | awk '{print $9}' | grep ".so"); do echo ""; echo "Lib Name: $i"; strings $i | grep "NTPSyncWithHost"; done
The above line will print the library name after this will run the strings command on the library to get any string has the word getWiFiApConfig and will print the results under the library name. Therefore, we will be able to know which library copy for us the device time or anything related. Command output:
Lib Name: app.so
Lib Name: cloudupdate.so
Lib Name: global.so
Lib Name: lan.so
Lib Name: product.so
Lib Name: system.so
NTPSyncWithHost
NTPSyncWithHost
Lib Name: upgrade.so
Lib Name: wireless.so
Lib Name: wps.so
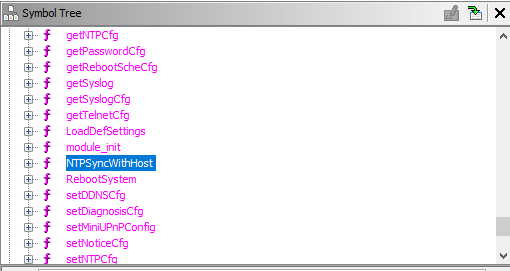
And as we can see it’s with-in the system.so library, As we did with the cstecgi.cgi file. Let’s do the same with the library with Ghidra. After opening the Functions tab under Symbol Tree we can notice the NTPSyncWithHost function:
So, We can say the flaw is as the following:
As we can see the function is a small function:
Now, Let’s understand what this function do and how it works. First the function start by taking 3 parameters:
void NTPSyncWithHost(undefined4 param_1,undefined4 param_2,undefined4 param_3)
Then, We can see Declare variables used within the function:
undefined4 uVar1;
FILE *__stream;
int iVar2;
char acStack_288 [256];
undefined4 local_188;
timeval local_184;
char acStack_17c [100];
char acStack_118 [256];
-
uVar1: an undefined4 type variable. -
__stream: a pointer to a FILE object. -
iVar2: an integer variable. -
acStack_288: a character array of size 256. -
local_188: an undefined4 type variable. -
local_184: atimevalstruct (used to represent time intervals). -
acStack_17c: a character array of size 100. -
acStack_118: a character array of size 256.
uVar1 = websGetVar(param_2,0x6110,0x6164);
memset(acStack_17c,0,100);
gettimeofday(&local_184,(__timezone_ptr_t)0x0);
After that Call the websGetVar() function with parameters param_2, 0x6110, and 0x6164, then store the result in uVar1. The websGetVar function is used to get the value of a variable from a web form submitted by a user. The two hexadecimal values 0x6110 and 0x6164 are string pointers representing variable names, which the function will search for in the submitted form. memset() function is to fill the acStack_17c character array with 0's, initializing it with a size of 100. After that gettimeofday() function with the address of the local_184 timeval struct and a null timezone pointer ((__timezone_ptr_t)0x0) and get the current time and stores it in the timeval struct local_184. So, we can see that the uVar1 carry the value of HostTime parameter. Now, Let’s rename it to HostTime.
__stream = fopen((char *)0x611c,(char *)0x5db4);
if (__stream != (FILE *)0x0) {
fscanf(__stream,(char *)0x5e70,acStack_118);
iVar2 = atoi(acStack_118);
fclose(__stream);
sprintf(acStack_17c,(char *)0x6134,local_184.tv_sec - iVar2);
system(acStack_17c);
}
In these lines, the fopen() function is called with two parameters, (char *)0x611c and (char *)0x5db4 and these two hexadecimal values are string pointers representing the file name and the file opening mode, respectively. The function opens the specified file and returns a FILE pointer which is stored in the __stream variable. If the file cannot be opened, fopen() will return a null pointer, Then it checks if __stream is not equal to a null pointer ((FILE *)0x0). If it is not null, that means the file has been successfully opened and the code inside the if statement will be executed which is a call to fscanf() function to read data from the opened file __stream, The function reads data according to the format specified by the string pointer (char *)0x5e70 and stores the result in the acStack_118 character array. The format string is a string that specifies how the data should be parsed from the file. Then atoi() function to convert the string in acStack_118 to an integer and store the result in the iVar2 variable. Finally, Close the opened file by calling the fclose() function with the __stream parameter and call the sprintf() function to format a string and store it in acStack_17c variable & Call the system() function to execute the value in acStack_17c variable. By moving to the following lines:
iVar2 = Validity_check(HostTime);
if (iVar2 == 0) {
sprintf(acStack_288,(char *)0x6158,HostTime);
CsteSystem(acStack_288,0);
apmib_set(0x97,&local_188);
apmib_update_web(4);
system((char *)0x6168);
websSetCfgResponse(param_1,param_3,0x5f40,0x5b88);
system((char *)0x6180);
}
Here we can see Call the Validity_check() function with HostTime as a parameter, This function likely checks the validity of the NTP server address obtained from the web request and store the result in the iVar2 variable. After that the IF condition checks if iVar2 is equal to 0, If it is, this means the NTP server address is valid and the code inside the if statement will be executed. By using the sprintf() function to format a string and store it in the acStack_288 character array. The format string is specified by the string pointer (char *)0x6158 and the NTP server address HostTime is used as an argument to fill the placeholders in the format string, Then calling the CsteSystem() function with the acStack_288 character array and 0 as parameters and this function is a custom function made by the developer to run a system command to update the NTP server configuration with the user-specified server address which include our HostTime parameter value. After that, call apmib_set() function with 0x97 and the address of local_188 as parameters and sets a value in the Application MIB (Management Information Base) database. Call the apmib_update_web() function with 4 as a parameter to update the web-based configuration interface to reflect the changes made to the NTP server configuration. After all of this we can see that the issue occurs at the following lines:
sprintf(acStack_288,(char *)0x6158,HostTime);
CsteSystem(acStack_288,0);
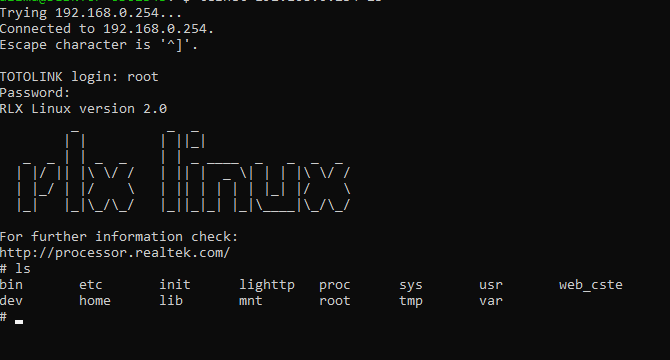
As there is no filtration to the user input and the parameter value can be manipulated by the user. It’s time to exploit it. I connected the device through telnet services first:
Now, Let’s go to Burp Suite and manipulate the request and show a PoC for the vulnerability:
As we can see in the above screenshot we were able to execute the command successfully.
Final Thoughts
The developer shall use an Asp endpoint to operate the time on the device as a different option instead of executing commands to do it. But, In our case of this code there are many solutions to make sure it will be hard for the user to escape the default command and inject malicious command using regex to check for a valid date as the following:
void NTPSyncWithHost(undefined4 param_1,undefined4 param_2,undefined4 param_3)
{
undefined4 HostTime;
FILE *__stream;
int iVar1;
char acStack_288 [256];
undefined4 local_188;
timeval local_184;
char acStack_17c [100];
char acStack_118 [256];
regex_t regex;
int regex_status;
// Compile the regular expression
regex_status = regcomp(®ex, "^[0-9]{4}-[0-9]{2}-[0-9]{2} [0-9]{2}:[0-9]{2}:[0-9]{2}$", REG_EXTENDED);
if (regex_status) {
printf("Could not compile regex.\n");
return 1;
}
local_188 = 0;
HostTime = websGetVar(param_2,0x6110,0x6164);
memset(acStack_17c,0,100);
gettimeofday(&local_184,(__timezone_ptr_t)0x0);
__stream = fopen((char *)0x611c,(char *)0x5db4);
if (__stream != (FILE *)0x0) {
fscanf(__stream,(char *)0x5e70,acStack_118);
iVar1 = atoi(acStack_118);
fclose(__stream);
sprintf(acStack_17c,(char *)0x6134,local_184.tv_sec - iVar1);
system(acStack_17c);
}
// Check if the HostTime variable matches the regex pattern
regex_status = regexec(®ex, HostTime, 0, NULL, 0);
if (!regex_status) {
iVar1 = Validity_check(HostTime);
if (iVar1 == 0) {
sprintf(acStack_288,(char *)0x6158,HostTime);
CsteSystem(acStack_288,0);
apmib_set(0x97,&local_188);
apmib_update_web(4);
system((char *)0x6168);
websSetCfgResponse(param_1,param_3,0x5f40,0x5b88);
system((char *)0x6180);
} else {
return 1;
}
}
return;
}
Here we used regex to check the patterns of the date if it’s valid or no, If it’s not valid it will exit without executing anything. But, If it’s valid then it will execute the code normally.
Conclusion
In this analysis we had a look on CVE-2021-42890 and highlighted the issue made by the developer & Provided a solution that can help in mitigating the issue. Finally, You could use any other decompiler other than Ghidra as it’s not making the codes more clear.
References
-
https://www.totolink.net/home/news/me_name/id/39/menu_listtpl/DownloadC.html
-
https://ghidra-sre.org/