Bypass The Anti-Virus - Part 2: Common Misconfigurations, Techniques & Attacks
Introduction
After the basics we discuss in the previous part of this series. Now, it’s the time to move forward and know about the Misconfigurations, Techniques & Attacks that can affect the anti-virus. Taking the Misconfigurations topic first. To be more clear, Any software could have some misconfigurations during the development & implementation of the software. Therefor, as the anti-virus also a software it can be affected to the misconfigurations we will discuss.
Insecure Permissions
Insecure Permissions Occaures when a low-privileges user “Non-Administrators” get permissions he doesn’t suppose to have it. Before the example the permissions are as the following Read,Write,Execute and could be all “Full Control”.
Read: View & Ability to read a file and it’s containtWrite: Ability to write “Edit” and modify.Execute: Ability to execute and run the file/program.
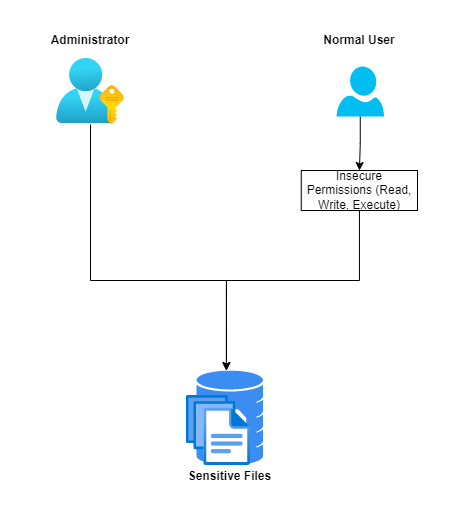
So, any of these misconfigurations related to the permissions known as Insecure Permissions can result in Reading, Wrting & Executing on sensitive files and programs for example:
- Insecure
Readpermissions could apper in reading configuration files of the anti-virus as an example. - Insecure
Writepermissions could apper in modifying the anti-virus configuration files or the affected files at all. For example theSignatures Databasefile could be deleted or making it empty therefore theStatic Enginewill fail to detecting the malware. - Insecure
Executepermissions can lead to executing of dangerous executables like uinstall program which will lead to remove the anti-virus.Improper Privileges
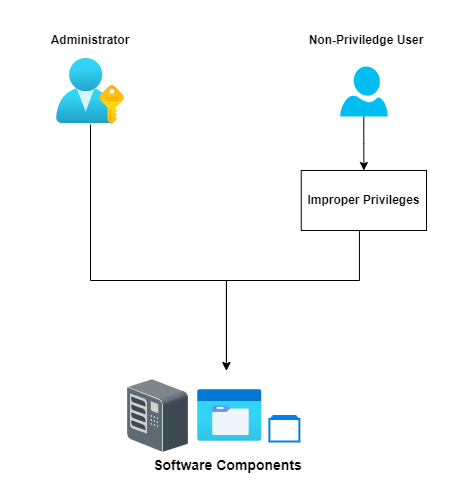
Another misconfiguration is Improper Privileges and here the software “Anti-Virus” itself doesn’t check for the user privileges (If ths user is allowed or not). As a results that will let a non-privileged user to access/modify the software and its related components.This type of misconfigurations could also lead to Privilige Escalation. You can read about Improper Privileges from here. And you can see somecases found in some Endpoint Security Softwares: Bitdefender, McAfee,.
Unquoted Service Path
The Unquoted Service Path is one of the misconfiguration on the Windows Platform and this kind of misconfigurations is well-known, because it’s widely used to Escalate Priviliges. Let’s Explain the idea behind the service path more to make it clear. When we create a windows service manually or when we install a software, The software create some services that are responable to run some binaries or some files when the service boot-up, Therefor, the software can work well without any problems as each service run a specific binary or file that has specific funcation/operation in the anti-virus.
We can search for the Services App in the taskbar search:

After open it we can open any services to explain how it works:
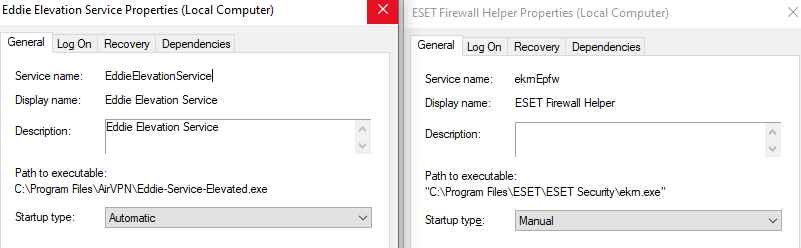
In the Above picture you can see that we got 2 Services with the following 2 paths under Path to executable or as it called binpath:
- Eddie Services:
C:\Program Files\AirVPN\Eddie-Service-Elevated.exe - ESET Services:
"C:\Program Files\ESET\ESET Security\ekrn.exe"
So, As you can see the Eddie Services has the path without any quotes like '' or "". Unlike ESET Services has double quotes "". Now, Why do we need to put the path inside quotes ?. To know the answer let’s explain how Windows execute the Service binary. When there are spaces in the path, Windows try to execute the path as the following:
Taking the following path for example C:\Program Files\vsociety software\run.exe. Basiclly, as there is no qoutes, It will replace the spaces and read it as a path and would add .exe to it and try to execute it if not exist will move to the next one until the end of the path reached.
Process example as the following for the pervious 2 paths:
C:\Program Files\vsociety software\run.exe:C:\Program.exe: If not exist the following step:C:\Program Files\vsociety.exe: If not exist the it will run the original one which is the followingC:\Program Files\vsociety software\run.exe: it will run as its the targeted original existing file.
As we saw if a malicious user created a file called a malicious file called Program.exe under C directory. the service will execute it. As a results, it will launch the malicious file instead of the targeted service file. Therefor, it could lead to stop some features in the anti-virus as the service binary is important and needed to start some protections.
"C:\Program Files\vsociety software\run.exe": the qouted path cancel the spaces part and tell that this is a full path.
DLL Hijacking
A DLL (Dynamic-link library) file is a library can be found in windows and it’s contains functions and codes that do a spesific task to do. Basically, works as any other library exist. These DLLs can be hijacked and trick the software to load a DLL file created by the malicious user which gonna lead to a damage or to make the software loss some features. In case of Anti-Virus, It could be an important library to do some scans or detect malware. As a results, it’s gonna lead to a bypass.
DLL Hijacking got a lot of types as the following:
DLL replacement: replace a legitimate DLL with an evil DLL. This can be combined with DLL Proxying , which ensures all functionality of the original DLL remains intact.DLL search order hijacking: DLLs specified by an application without a path are searched for in fixed locations in a specific order. Hijacking the search order takes place by putting the evil DLL in a location that is searched in before the actual DLL. This sometimes includes the working directory of the target application.Phantom DLL hijacking: drop an evil DLL in place of a missing/non-existing DLL that a legitimate application tries to load.DLL redirection: change the location in which the DLL is searched for, e.g. by editing the %PATH% environment variable, or .exe.manifest / .exe.local files to include the folder containing the evil DLL.WinSxS DLL replacement: replace the legitimate DLL with the evil DLL in the relevant WinSxS folder of the targeted DLL. Often referred to as DLL side-loading.Relative path DLL Hijacking: copy (and optionally rename) the legitimate application to a user-writeable folder, alongside the evil DLL. In the way this is used, it has similarities with (Signed) Binary Proxy Execution. A variation of this is (somewhat oxymoronically called) ‘bring your own LOLbin’ in which the legitimate application is brought with the evil DLL (rather than copied from the legitimate location on the victim’s machine).
The above types from hacktricks. And also you could read more about the DLL Hijacking itself from the same link.
Conclusion
We have learned about simple and little 4 of the Misconfigurations that could be used to bypass the anti-virus software, There are many and more other ways can be used to bypass the anti-virus software. These Misconfigurations, Techniques & Attacks we will be discussed in the coming parts. Always don’t forget to take a look around the outlines and understand more. But, at all we gonna go deep when we come to part 5 of the series, where we gonna start to attack our Victim (Anti-Virus software vendor).